1. Introduction
Server virtualization is a technology that divides the resources of a physical server into multiple virtual servers, aiming to improve the utilization rate and management efficiency of computing resources. With the increasing demand for IT infrastructure from enterprises, virtualization technology has become an important part of modern data centers. This article will introduce the concepts, technical architecture, advantages, and implementation schemes of server virtualization.
2. Server Virtualization Concept
Server virtualization installs virtualization software on a physical server, allowing multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run concurrently on a single physical machine. Each virtual machine has an independent operating system and applications, achieving resource sharing and isolation.
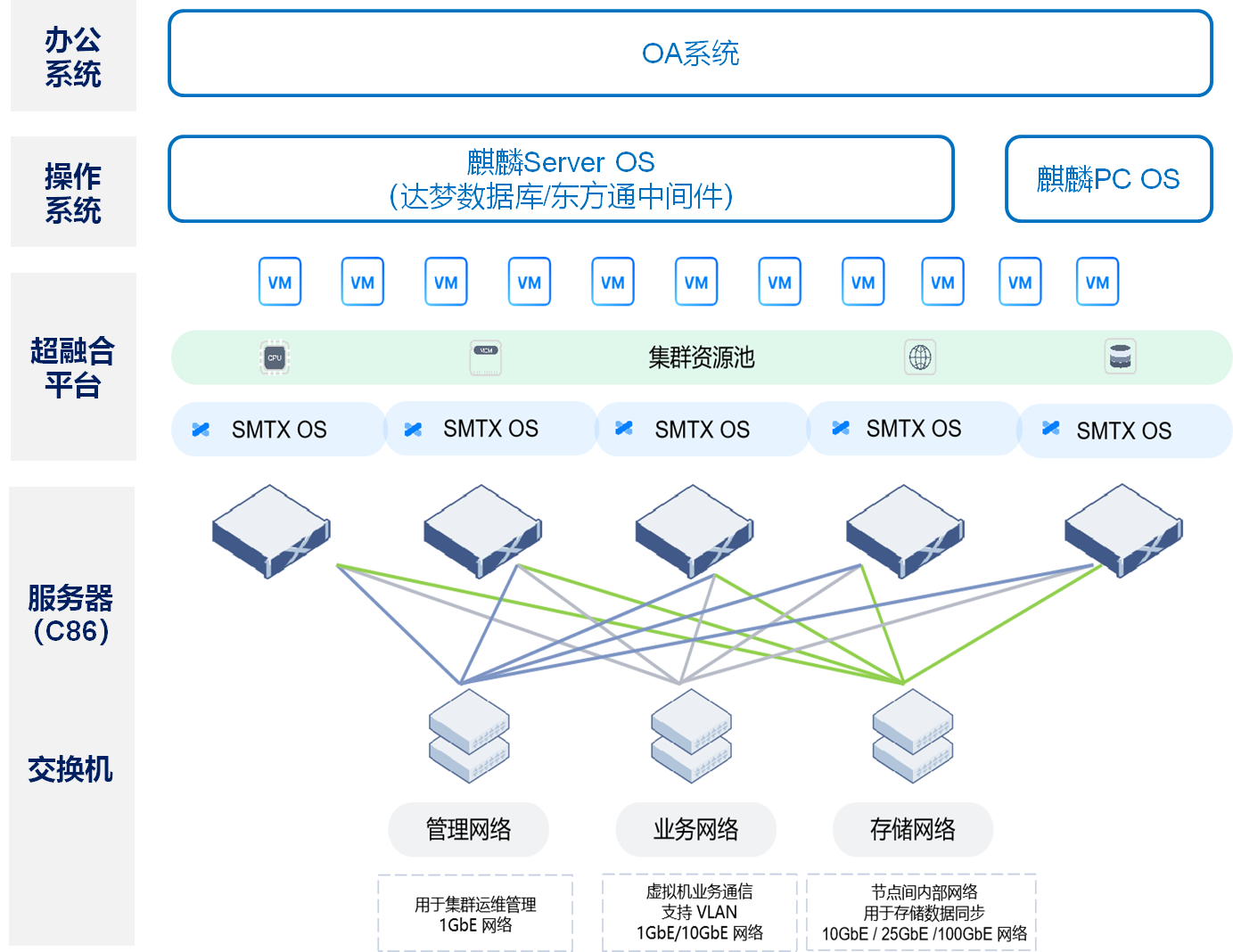
3. Technical Architecture
Server virtualization solutions typically include the following key components:
Virtualization layer (Hypervisor): Also known as a virtual machine monitor, it is responsible for managing and allocating physical resources to various virtual machines. Common Hypervisors include VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM.
Physical server: Provides the underlying hardware for computing, storage, and network resources.
Management tools: Tools used to monitor and manage the virtualization environment, such as VMware vCenter and Microsoft System Center.
Storage solution: Provides shared storage for virtual machines, ensuring high data availability and fast access.
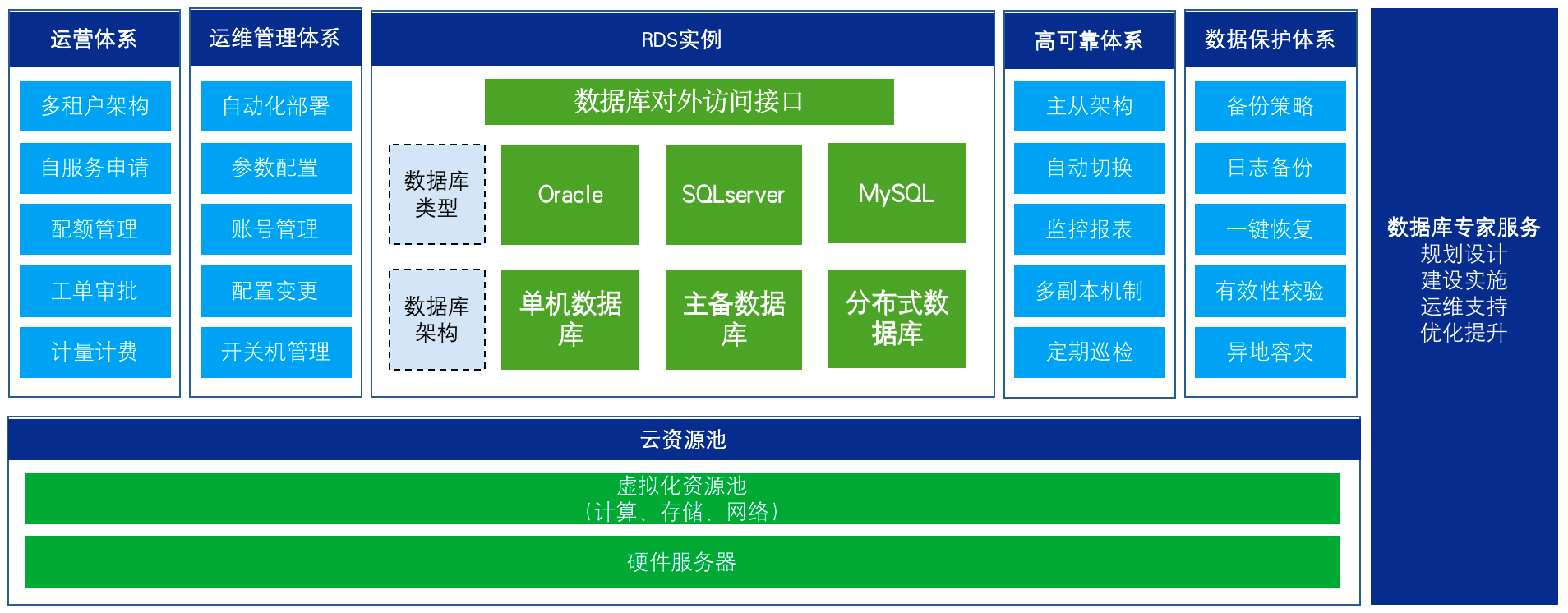
4. Solution Advantages
4.1 Improved Resource Utilization
By deploying multiple virtual machines on the same physical server, server virtualization can significantly improve the utilization rate of hardware resources and reduce wasted idle resources.
4.2 Reduced Costs
Virtualization reduces the number of physical servers, thereby reducing costs associated with hardware procurement, maintenance, and energy consumption. Simplified management and automation features also reduce operational costs.
4.3 Flexibility and Scalability
The virtualization environment allows for the rapid deployment and modification of virtual machines to meet changing business needs. The system can be scaled horizontally or vertically at any time to add new virtual machines or resources.
4.4 Disaster Recovery and High Availability
Server virtualization supports fast backup and recovery mechanisms, allowing virtual machine snapshots to be saved to storage to ensure data security. In addition, high availability can be achieved using load balancing and failover technologies.
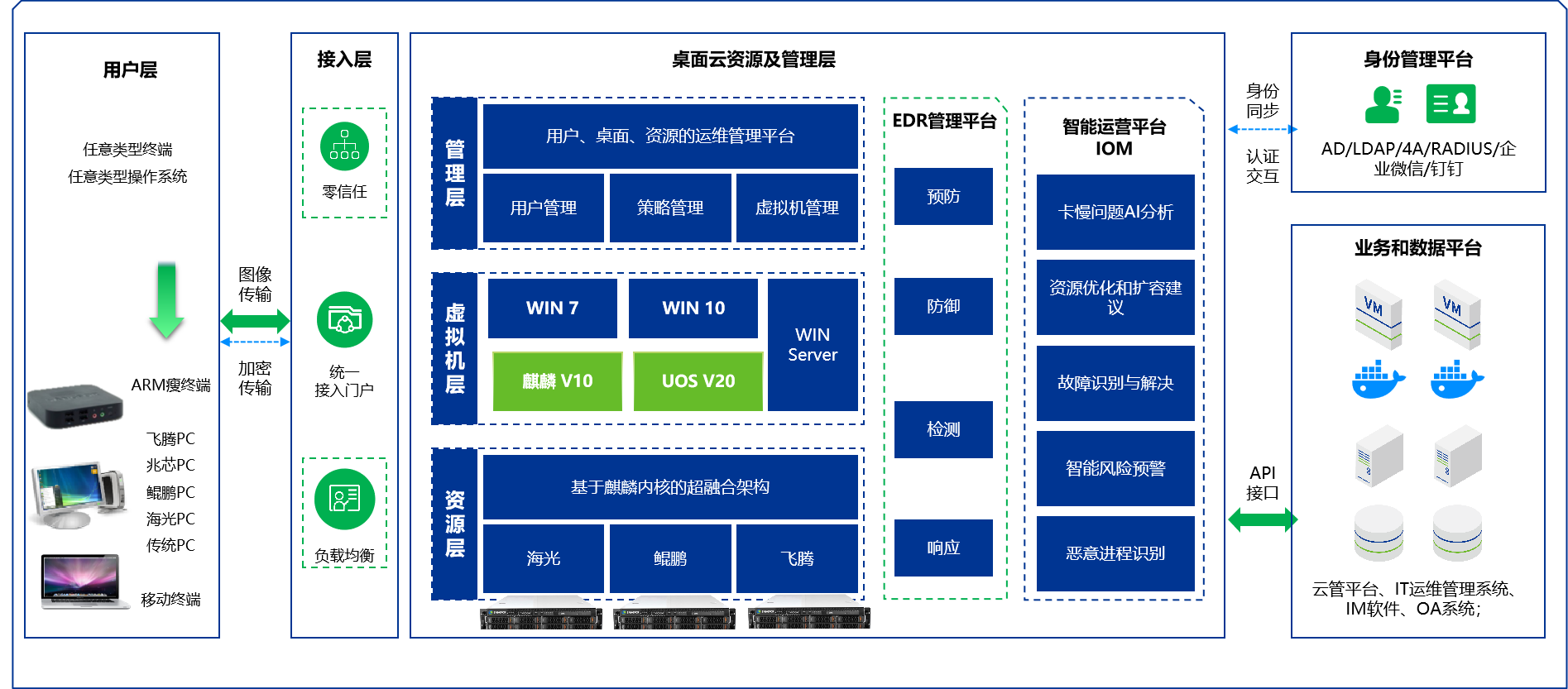
5. Implementation Scheme
5.1 Assessment and Planning
- Needs analysis: Assess existing infrastructure and determine virtualization needs.
- Resource planning: Predict the number of virtual machines and performance requirements, and plan physical server configurations.
5.2 Environment Setup
- Select a suitable virtualization platform: Choose the appropriate virtualization technology (such as KVM, VMware, or Hyper-V) based on enterprise needs.
- Install and configure Hypervisor: Install virtualization software on the physical server and perform initial configuration.
5.3 Migration and Deployment
- Virtual machine creation: Create and configure virtual machines as needed.
- Data migration: Migrate existing applications and data to new virtual machines.
5.4 Management and Monitoring
- Use management tools: Implement centralized management and monitoring to ensure the stability of the virtualization environment.
- Regular maintenance: Regularly inspect and optimize the virtualization environment to ensure system performance.
Other Solutions
Systematized Data Disaster Recovery
2025-08-14
2025-08-14
Store anti-ransomware solutions
2025-08-14
High-performance NAS storage solution
2025-08-14
2025-08-06
2025-08-05
Service and technical support solutions
2025-08-05
2025-08-05
Xinchuang OA Full-Stack Solution
2025-05-30
Desktop virtualization solution
2025-04-23